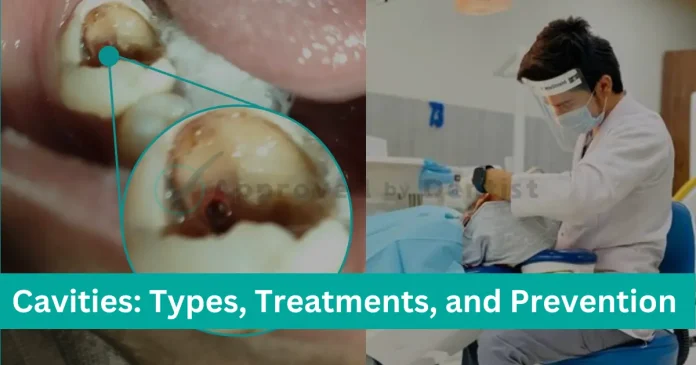
Cavities, also known as dental caries, are a common dental issue affecting individuals of all ages worldwide.
These dental cavities are essentially decayed areas in the teeth, resulting from a combination of factors, including poor oral hygiene, bacterial activity, and dietary habits.
Understanding the types, treatments, and prevention methods for cavities is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health.
Types of Cavities
Pit and Fissure Cavities:
Pit and fissure cavities are commonly found on the chewing surfaces of molars and premolars.
These cavities occur when plaque accumulates in the deep grooves and fissures of the teeth, making them vulnerable to decay.
Regular brushing and dental sealants can help prevent pit and fissure cavities.
Smooth Surface Cavities:
Smooth surface cavities develop on the flat surfaces of the teeth, particularly between the teeth or along the gumline.
Poor oral hygiene and the consumption of sugary or acidic foods and beverages contribute to the formation of these cavities.
Flossing and using fluoride toothpaste are essential for preventing smooth surface cavities.
Root Cavities:
Root cavities occur on the roots of the teeth, typically in individuals with receding gums or periodontal disease.
These cavities expose the tooth roots to bacteria and decay, leading to sensitivity and pain.
Maintaining good gum health through proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups can help prevent root cavities.
Treatment Options for Cavities
Fillings:
Dental fillings are the most common treatment for cavities. During this procedure, the decayed portion of the tooth is removed, and the cavity is filled with a durable material such as composite resin, amalgam, or gold.
Fillings restore the tooth’s structure and function while preventing further decay.
Root Canal Therapy:
Root canal therapy may be necessary for cavities that have progressed to the innermost layer of the tooth.
The infected pulp tissue is removed during this procedure, and the root canal is cleaned, filled, and sealed.
Root canal therapy helps save the natural tooth and alleviates pain and infection.
Crowns:
In cases where a cavity is extensive and has weakened the tooth structure, a dental crown may be recommended.
Crowns are custom-made caps that cover the entire visible portion of the tooth, providing strength, protection, and aesthetic improvement.
Extraction:
Extraction may be the only option in severe cases of decay or when a tooth is beyond repair.
Extracting the affected tooth can prevent further damage and infection, preserving surrounding teeth and overall oral health.
Prevention Tips for Cavities
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene:
Brushing teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily helps remove plaque and food particles, reducing the risk of cavities.
Limit Sugary and Acidic Foods:
Reducing the consumption of sugary snacks and acidic beverages can minimize the exposure of teeth to harmful bacteria and acids, thus lowering the risk of cavities.
Regular Dental Check-ups:
Routine dental examinations and cleanings are essential for detecting cavities early and preventing their progression.
Dentists can provide professional cleanings, fluoride treatments, and preventive care to maintain oral health.
Use Fluoride Products:
Fluoride toothpaste, mouthwash, and professional fluoride treatments help strengthen tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay and cavities.
Consider Dental Sealants:
Dental sealants are protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of molars and premolars to seal off pits and fissures, preventing bacteria and food particles from accumulating and causing cavities.
Conclusion:
Cavities are a prevalent dental issue that can lead to pain, infection, and tooth loss if left untreated.
By understanding the types of cavities, available treatment options, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain optimal oral health and prevent the development of cavities.