Used Serviceable Material (USM) market
The aviation industry is a cornerstone of global connectivity, enabling the rapid movement of people and goods across continents. However, this industry also faces significant challenges in terms of environmental impact. As climate change and sustainability become increasingly urgent concerns, the aviation sector is under pressure to adopt greener practices. This post explores the strides being made towards sustainable aviation, focusing on innovative technologies, policy measures, and the role of stakeholders in driving this transformation.
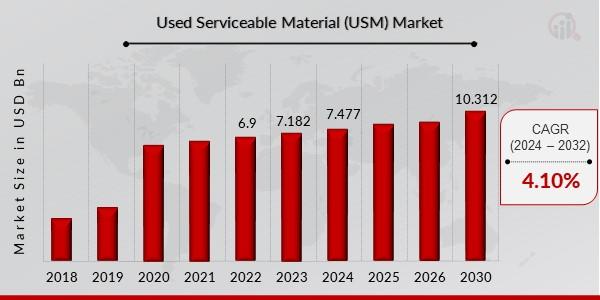
The Used Serviceable Material (USM) market was valued at USD 7.1829 billion in 2023. This industry is anticipated to grow from USD 7.4774 billion in 2024 to USD 10.3123 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.10% during the forecast period (2024 – 2032).
The Environmental Challenge
Aviation contributes approximately 2-3% of global carbon dioxide emissions, with the potential for significant increases as air travel continues to grow. The environmental impact extends beyond carbon emissions to include noise pollution, water usage, and the impact of airport operations on local ecosystems. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates technological innovation, regulatory frameworks, and collaboration across the industry.
Technological Innovations
One of the most promising avenues for reducing the environmental footprint of aviation is through technological innovation. Several key areas are being explored:
- Fuel Efficiency and Alternative Fuels
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs): These biofuels are derived from renewable sources like plant oils, algae, and waste products. SAFs can reduce lifecycle carbon emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuel. Airlines such as Delta and United have begun integrating SAFs into their operations, demonstrating the feasibility of this approach.
- Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft: Hydrogen fuel cells and combustion engines powered by hydrogen offer a zero-emission alternative. Airbus has announced plans to develop the world’s first zero-emission commercial aircraft by 2035, highlighting the potential of hydrogen as a sustainable aviation fuel.
- Electric Propulsion
- Electric and Hybrid-Electric Aircraft: Companies like Pipistrel and Eviation are pioneering electric aircraft for short-haul flights. These aircraft produce no direct emissions and can significantly reduce noise pollution. Hybrid-electric aircraft, combining electric propulsion with traditional engines, are also being developed for longer ranges.
- Advanced Aerodynamics and Lightweight Materials
- Aerodynamic Enhancements: Innovations such as winglets, advanced wing designs, and more efficient flight paths can reduce fuel consumption. NASA and Boeing’s development of the Transonic Truss-Braced Wing concept aims to achieve substantial efficiency gains.
- Lightweight Materials: The use of composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, can significantly reduce aircraft weight, leading to lower fuel consumption. Boeing’s 787 Dreamliner and Airbus’s A350 XWB are examples of aircraft that leverage these advanced materials.
Regulatory and Policy Measures
Governments and international organizations play a crucial role in driving the adoption of sustainable practices in aviation. Key initiatives include:
- International Agreements
- CORSIA (Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation): Implemented by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), CORSIA aims to stabilize CO2 emissions from international aviation at 2020 levels. Airlines are required to offset any emissions above this baseline through carbon credits and other measures.
- EU Emissions Trading System (ETS): The EU ETS includes aviation within its cap-and-trade system, requiring airlines to hold emissions allowances for their flights within the European Economic Area. This incentivizes airlines to reduce emissions and invest in more efficient technologies.
- National Policies
- Incentives for Sustainable Aviation Fuels: Governments can provide financial incentives, such as tax credits and grants, to encourage the production and use of SAFs. The U.S. and European countries have introduced measures to support SAF development and integration.
- Research and Development Funding: Public funding for R&D in sustainable aviation technologies can accelerate innovation. Initiatives like the FAA’s Continuous Lower Energy, Emissions, and Noise (CLEEN) program in the U.S. and the Clean Sky program in Europe are critical in this regard.
The Role of Stakeholders
Achieving sustainability in aviation requires collaboration among a diverse set of stakeholders, including airlines, manufacturers, airports, policymakers, and passengers.
- Airlines
- Operational Efficiency: Airlines can adopt operational measures to improve efficiency, such as optimizing flight routes, reducing taxiing time, and implementing best practices for fuel management.
- Fleet Modernization: Investing in newer, more fuel-efficient aircraft can significantly reduce emissions. Many airlines are accelerating the retirement of older, less efficient models in favor of modern aircraft.
- Manufacturers
- Innovative Design: Aircraft manufacturers must continue to push the boundaries of design and engineering to create more sustainable aircraft. Collaboration with research institutions and technology companies is essential to drive innovation.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Ensuring that the supply chain is environmentally responsible is also crucial. This includes sourcing materials sustainably and minimizing waste and emissions during manufacturing processes.
- Airports
- Green Infrastructure: Airports can implement green building practices, such as using renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and reducing water consumption. LEED certification and other sustainability standards can guide these efforts.
- Sustainable Ground Operations: Electrifying ground support equipment, optimizing ground traffic management, and implementing waste reduction programs can significantly lower an airport’s environmental impact.
- Passengers
- Eco-Friendly Choices: Passengers can make a difference by choosing airlines that prioritize sustainability, offsetting the carbon emissions of their flights, and supporting policies and initiatives aimed at reducing aviation’s environmental footprint.
Conclusion
The transition to sustainable aviation is a complex and challenging journey, but it is also a necessary one. Technological innovations, robust regulatory frameworks, and collaborative efforts among stakeholders are key to achieving greener skies. As the industry continues to evolve, the commitment to sustainability will not only benefit the environment but also ensure the long-term viability of aviation as a critical component of global connectivity. The path to sustainable aviation is not without its hurdles, but with concerted effort and innovation, a greener future for air travel is within reach.
About US
Market Research Future (MRFR) is a global market research company that takes pride in its services, offering a complete and accurate analysis with regard to diverse markets and consumers worldwide. Market Research Future has the distinguished objective of providing the optimal quality research and granular research to clients. Our market research studies by products, services, technologies, applications, end users, and market players for global, regional, and country level market segments, enable our clients to see more, know more, and do more, which help answer your most important questions.
Contact us:
Market Research Future (part of Wantstats Research and Media Private Limited),
99 Hudson Street,5Th Floor New York 10013, United States of America
Sales: +1 628 258 0071 (US) +44 2035 002 764 (UK)